The impact of economic sanctions on global trade

The impact of economic sanctions on global trade disrupts market access for exporters and importers, leading to economic hardship and financial losses while being enforced by international organizations to promote political and social change.
The impact of economic sanctions on global trade is more profound than many realize. You might be surprised at how these measures shift market relationships and economic fortunes. Have you ever thought about the ripple effects they create worldwide?
Understanding economic sanctions and their purpose
Understanding economic sanctions and their purpose is crucial for grasping how nations interact on the global stage. Sanctions are powerful tools used to influence the behavior of other countries. They can affect economies in various ways, from trade restrictions to financial measures.
Economic sanctions typically aim to achieve specific political or social objectives. They can be applied in situations of conflict, human rights abuses, or other significant international issues. Understanding their impact requires a closer look at how they function and the intended outcomes.
Types of Economic Sanctions
There are several types of economic sanctions, and each serves a different goal.
- Trade sanctions: These limit or prohibit trade with specific countries.
- Financial sanctions: These restrict access to financial markets or institutions.
- Travel bans: These prevent individuals from entering certain countries.
- Asset freezes: These block access to funds and property held in specific locations.
These measures can significantly impact the targeted country’s economy and its citizens. Trade sanctions, for example, can lead to shortages of essential goods and a rise in prices. They can also disrupt supply chains, affecting not only the sanctioned nation but also those engaged in trade with it.
Another important factor is the role of international organizations in implementing sanctions. Bodies like the United Nations often create and enforce these measures in response to global issues. Their decisions reflect the collective will of member states, which can lend credibility to the sanctions.
Intended Outcomes of Sanctions
The intended outcomes of economic sanctions vary, but the ultimate goal is often to change the behavior of the targeted country or regime. By increasing economic pressure, sanctions aim to compel political change, such as achieving compliance with international laws or ending human rights violations.
However, the effectiveness of sanctions can be debated. Sometimes, they succeed in prompting dialogue and negotiations. Other times, they can entrench existing regimes and hurt the civilian population more than the government. The balance between impact and intention is delicate and complex.
In conclusion, understanding economic sanctions and their purpose provides essential insight into international relations. As global dynamics continue to evolve, so too will the mechanisms used to enforce them, highlighting the ongoing need for study and analysis.
Effects of sanctions on exporters and importers
The effects of sanctions on exporters and importers can be profound and far-reaching. When sanctions are imposed, they alter the way businesses conduct trade and can lead to significant financial losses. Understanding these impacts helps illuminate the challenges faced in international commerce.
Sanctions often restrict the flow of goods, affecting exporters who rely on specific markets. For these businesses, the immediate impact can include reduced sales and disrupted supply chains. Many exporters may struggle to find alternative markets, causing long-term financial strain.
Challenges for Exporters
Exporters face several challenges due to sanctions:
- Market loss: Access to certain markets may be completely cut off.
- Financial penalties: Exporters could incur fines or penalties for inadvertently violating sanctions.
- Reputation damage: Being associated with sanctions can harm a company’s reputation.
- Operational disruptions: Logistics and shipping can become significantly more complicated.
On the flip side, importers are not spared from the severe effects of sanctions. They also face restrictions in the flow of goods, which can hinder access to necessary resources. Prices may rise, and availability of products can dwindle, forcing importers to seek alternatives.
Impact on Importers
Importers endure various issues when sanctions are active:
- Increased costs: Finding new suppliers can lead to higher prices.
- Supply shortages: Certain goods may become scarce, impacting inventory levels.
- Legal complexities: Navigating the legal landscape involving sanctions can be daunting and requires vigilance.
The ripple effects of these challenges extend beyond individual businesses. Suppliers, service providers, and even consumers feel the weight of these sanctions. As trade routes are altered, entire economies can shift, leading to widespread ramifications.
Thus, understanding the overall impact of sanctions on exporters and importers is vital for grasping the changing landscape of global trade. The shifting market dynamics underscore the importance of strategic planning and adaptability for businesses in today’s economic climate.
The role of international organizations in sanctions

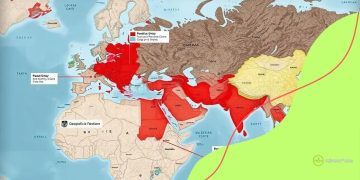
The role of international organizations in sanctions is significant and multifaceted. These bodies help shape, implement, and enforce sanctions aimed at maintaining global peace and security. Their authority is crucial in coordinating international responses to various issues, such as conflicts and human rights violations.
Organizations like the United Nations (UN) and the European Union (EU) play key roles in this context. They analyze situations and often issue sanctions that member states are encouraged to follow. This collective action enhances the legitimacy of the measures imposed, making them more effective.
United Nations Sanctions
The UN Security Council is responsible for imposing sanctions on nations that threaten peace. These sanctions can take various forms:
- Economic sanctions: These limit trade and financial transactions with the targeted country.
- Travel bans: These prevent key individuals from entering other countries.
- Arms embargoes: These restrict the supply of weapons to certain nations.
By using these tools, the UN seeks to pressure governments into changing their behavior without resorting to military conflict. The ability to unify the global community behind these measures is a powerful aspect of their effectiveness.
European Union Policies
The European Union also plays an active role in sanctions. The EU can implement its own measures that align with those of the UN or address specific political issues. For instance, the EU often applies sanctions in response to human rights abuses or to promote democracy.
These actions can impact countries significantly, demonstrating the EU’s commitment to international law and human rights. When the EU collaborates with other international organizations, the results can be even more impactful.
In summary, international organizations are pivotal in the process of imposing sanctions. Their involvement not only adds legitimacy but also fosters a collaborative approach to addressing global challenges, making it essential to understand their influence in this area.
Case studies: Countries most affected
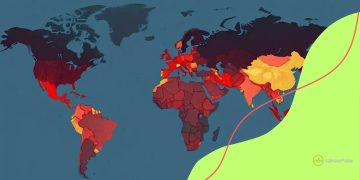
Examining case studies of countries most affected by economic sanctions helps to illustrate their real-world impacts. Various nations experience sanctions differently, depending on their economic structures, political climates, and relationships with other countries.
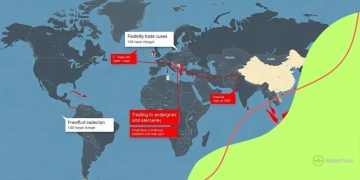
One significant example is Iran. Sanctions imposed due to its nuclear program have led to sharp declines in oil exports, severely crippling its economy. This situation has resulted in inflation and reduced access to foreign goods, affecting everyday life for its citizens.
Cuba’s Ongoing Struggles
Cuba has faced an ongoing embargo from the United States for decades. This comprehensive trade ban has led to shortages of food, medicine, and essential supplies, forcing Cubans to rely heavily on the state for goods. The challenges faced by the Cuban people highlight the long-term effects of sustained sanctions on a nation’s economy.
North Korea’s Isolation
Another notable case is North Korea. International sanctions due to its nuclear tests have isolated the country even further. While these sanctions aim to pressure the regime to denuclearize, they have also led to humanitarian issues, with food shortages becoming increasingly common as a result of restricted trade.
- Economic downturn: Countries under sanctions often see significant contractions in GDP.
- Increased poverty: Many citizens may experience levels of poverty that can increase due to unsustainable economies.
- Social effects: Public health can deteriorate as access to resources becomes limited.
These cases emphasize the complex nature of economic sanctions. While they are designed to address specific political issues, the collateral damage often affects the most vulnerable populations. It’s crucial to consider these impacts when discussing the efficacy and morality of sanctions.
Future trends in global trade and sanctions
Understanding the future trends in global trade and sanctions is crucial as the landscape of international relations continues to evolve. As economies become more interconnected, the effectiveness and application of sanctions are likely to adapt as well.
One significant trend is the increasing globalization of supply chains. This interconnectedness means that sanctions can have ripple effects across multiple countries. When sanctions are imposed, they can disrupt not just the target nation but also those involved in trade with it. As businesses become more aware of these risks, many are considering strategies to diversify their supply chains.
Rise of Digital Trade
Another trend is the rise of digital trade and e-commerce, which has transformed traditional trade practices. As more transactions take place online, ensuring compliance with sanctions becomes increasingly complex.
- Increased scrutiny: Companies may face greater scrutiny over their digital transactions to avoid inadvertently violating sanctions.
- Blockchain technology: Innovations like blockchain could offer solutions for ensuring transparency in trade.
- Virtual markets: The rise of virtual marketplaces could create unique challenges in identifying sanctioned entities.
Furthermore, the geopolitical landscape is shifting. As new economic powers arise, traditional alliances may be challenged, leading to changes in how sanctions are perceived and implemented. Countries may form new coalitions or adopt differing approaches to trade and sanctions, depending on their interests and economic strategies.
Climate Change and Sanctions
Another critical factor is climate change, which is increasingly influencing trade policies. Sanctions related to environmental issues may emerge as nations seek to hold each other accountable for climate commitments.
In conclusion, the future of global trade and sanctions is likely to be shaped by these trends. As the world adapts to new challenges and innovations, businesses must remain vigilant and flexible to navigate this changing landscape effectively.
The conclusion summarizes the insights gained from exploring the impact of economic sanctions on global trade. As we have seen, sanctions pose significant challenges for exporters and importers alike, affecting economies and individuals in profound ways. Additionally, the role of international organizations in enforcing sanctions cannot be underscored enough, as they help to maintain order and promote accountability on a global scale. Looking ahead, future trends indicate that trade dynamics will continue to evolve, influenced by globalization, technological advancements, and emerging geopolitical issues. Businesses and policymakers must remain adaptable to navigate this complex landscape for effective international commerce.
FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions about the Impact of Economic Sanctions on Global Trade
What are economic sanctions?
Economic sanctions are trade restrictions imposed by countries to influence the behavior of other nations or regimes.
How do sanctions affect exporters?
Sanctions can limit access to markets, reduce sales, and disrupt supply chains, leading to financial losses for exporters.
What role do international organizations play in sanctions?
International organizations like the UN and EU help implement and enforce sanctions to promote global peace and security.
What trends are shaping the future of global trade and sanctions?
Trends include globalization, increased digital transactions, and the potential for climate-related sanctions affecting trade dynamics.